Simplifying Life Insurance in India
What Is the Relationship Between Inflation and Unemployment?

source: imgix
Traditionally, inflation and unemployment have been inversely related to each other. However, this relationship is more intricate than it initially appears, and during the previous 50 years, it has failed several times.
In this blog, we will talk about the relationship between inflation and unemployment, two of the most carefully watched economic statistics, and how they impact the broader economy. Continue reading to know more about the same.
How Inflation and Employment Are Related?
A.W. Philips was the first to explain how unemployment and inflation are related. The Phillips curve illustrates the inverse relationship between the rates of unemployment and inflation. Inflation rises when unemployment rates decline. The relationship is asymmetrical and averse.
On a graph, the short-run Phillips curve has an L-shape when the unemployment rate is on the x-axis, and the inflation rate is on the y-axis.
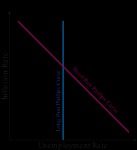
source: thismatter
The inflation rate might decline when unemployment increases. This happens because:
- An economy with a high unemployment rate will have weak labour unions and employee power. Then, it becomes difficult for companies to seek labour and wages as employers can hire other workers rather than paying high wages. In this regard, wage inflation might remain muted as unemployment rates are on the rise. As a result, both the price of products and services and the cost of manufacturing will decrease. Further, there is a reduction in both cost-push and demand-pull inflation.
- A high unemployment rate reflects a fall in economic activity. Businesses consequently experience an increase in the volume of unsold items and spare capacity. Businesses will face more price competition during a recession. Therefore, a lower output will unquestionably lower economic inflation, the demand-pull cause.
The 2000’s appear to be a collection of Phillips stages. 2001's short recession resulted in higher unemployment and marginally lower inflation. The years between 2003 and 2006 saw a decrease in the unemployment rate, with little growth in inflation on a yearly basis. Higher unemployment and a decrease in inflation were the main causes of the Great Recession, which started at the end of 2007.
What Are the Effects of Inflation on Employment?
The rise in unemployment does not always cause a decline in hiring. Employers immediately turn to cost-cutting measures to preserve their survival and profitability whenever a country has excessive inflation.
According to Santangelo, "Firms won't cut down hiring; they'll adapt the manner they hire." He anticipates that as a cost-cutting approach, firms will want to hire several part-time, contract, or "gig" workers than the usual practice of hiring a full-time worker to complete a job. They avoid paying for costly healthcare coverage as a result. Not to mention the money a business saves by moving to gig workers on the whole monthly cost, which includes incentives, a travel allowance, power, and more.
Employers immediately turn to cost-cutting measures to preserve their survival and profitability whenever a country has excessive inflation. And frequently, in order to save costs, businesses opt to use contract workers, gig workers, and freelancers. They avoid paying for costly healthcare coverage as a result.
What Are the Effects of Inflation on Workers with Low Wages?
The COVID-19 pandemic, which in many nations had the biggest impact on low-income groups, resulted in considerable salary losses for employees and their families. The cost-of-living crunch comes in addition to these wage losses.
Lower-income earners are more affected by rising inflation in terms of the cost of living. This is due to the fact that they spend the majority of their disposable income on necessities, which typically see higher price increases than non-essentials.
Despite nominal adjustments occurring, estimates reveal that in several countries for which statistics are available, rising price inflation is rapidly destroying the real worth of minimum wages.
What Is the Non Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment?
In macroeconomics, NAIRU, which stands for "non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment," refers to the level of unemployment in an economy at which inflation doesn't rise, i.e., it stays constant.
Inflation and unemployment (or employment) are two crucial macroeconomic variables. As demand increases as unemployment declines, inflation also increases. NAIRU is important in economics since it aids in the establishment of the government's employment-inflation equilibrium.
The Phillips Curve's depiction of an inverse association between inflation and unemployment was effective for the short term, particularly when inflation is relatively stable, as it was in the 1960s. Since the economy returns to its natural rate of unemployment and adjusts to any rate of inflation, it cannot be sustained over the long term. The economy has recently seen low unemployment, low inflation, and little wage growth.
FAQs About Inflation and Unemployment
Does inflation affect unemployment?
How does India lower unemployment?
In India, the regulatory bodies reduce unemployment in the following ways:
- Labour intensive methods
- Population control
- Encouraging self-employment
- Modifying the educational system
What is the need to solve unemployment?
How do inflation and unemployment affect my need for life insurance?
If I lose my job due to unemployment, should I still continue my term insurance policy?
Other Important Articles Related to Inflation and Financial Planning
Important Articles About Financial Planing




















