What is CRP (C-reactive Protein) in a Blood Test?

CRP, or C-reactive Protein, is a substance the liver produces in response to inflammation. When there is inflammation in the body, CRP or C-reactive protein levels increase. A basic blood test known as a C-reactive protein test is conducted to check the CRP level in a body.
This test will enable the identification of acute or chronic conditions causing inflammation, such as autoimmune disorders and infections. Continue reading this article to gain knowledge on CRP tests!

Table of Contents

What Is a C-reactive Protein Test?
C-reactive protein or CRP is a type of protein produced by the liver. This protein is sent to the bloodstream as a response to inflammation. The C-reactive protein test is the measurement of the CRP level in an individual’s blood.
Generally, a person has a low C-reactive protein level in their blood. A high level of CRP might be a sign of severe infection or any other medical disorder.
What Is the Need for a C-reactive Protein Test?
The CRP test might be done in order to monitor the conditions which cause inflammation. These conditions include –
- Bacterial infections like sepsis
- Fungal infections
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
- Osteomyelitis
Furthermore, if an individual has already been diagnosed, this test also helps to monitor the treatment.
When Should I Get the C-reactive Protein Test?
If you have inflammation symptoms such as swelling, fever of unknown origin, and pain, among others, then it is important to consider having a C-reactive protein (CPR) test. It is also used to monitor the course of chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
In addition, CRP testing may be performed to screen for infection and frame out your heart disease risk. Doctors may also use CRP levels to monitor recovery after treatment or surgery, offering insights into potential complications.
What is the Procedure for the C-reactive Protein Test?
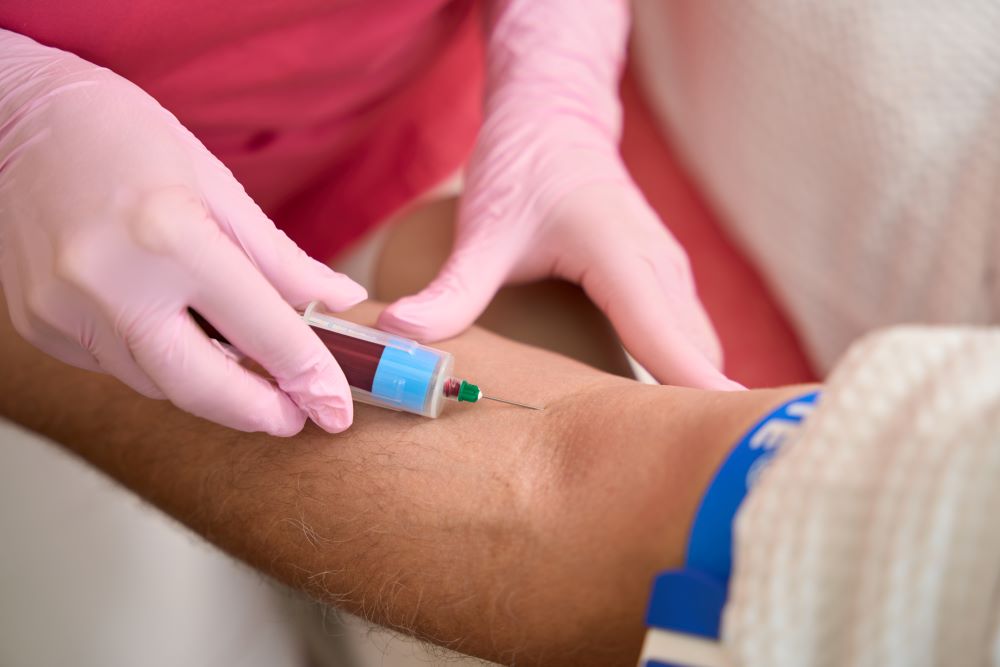
Usually, this examination requires drawing about 5 millilitres of blood from a vein in an arm. This sample will then be sent to a laboratory, where it will be analysed by looking at the level of C-reactive proteins found within your bloodstream.
The test is very simple; it takes just a few minutes, and you do not have to prepare anything special. This technique is least invasive, and blood drawing discomforts are usually transient.
How to Prepare for a C-reactive Protein Test?
Avoid doing strenuous excesses like a long run or intense weight training before the test. In case your blood is used for additional tests, the doctor might recommend you stop eating certain foods before a CRP test. Furthermore, certain medicines affect the CRP level.
Make sure to tell your doctor about the medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you take before the test. Adhering to these directions will ensure that your CRP measurements are accurate and, hence, a better understanding of your health status.
How is C-reactive Protein Measured in Blood Tests?
The quantity of CRP in your bloodstream can be determined using a blood test that directly measures its levels. A healthcare practitioner draws blood from your arm’s vein to perform the test. The collected specimen is then transported to the laboratory, where sophisticated equipment is used for analysis.
Laboratory reports give concentration results in terms of mg/L (milligrams per litre). Elevated levels indicate an ongoing body inflammation or infection. It is frequently used for assessing disease activity and responses to treatment.
How to Read the Results of the C-reactive Protein Test?
Generally, the result of a CRP test is measured in mg/dL or mg/L. In most cases, the doctor will explain to you the results of the test; however, in general:
Normal Range of C-reactive Protein in a Blood Test
Most people will have CRP levels between 0 and 10 mg/L, which is normal for all age groups, including adults, children, and infants. If CRP is elevated, then it could be indicative of inflammation or infection, whereas when it falls within this range, most likely, there isn’t any significant inflammatory condition.
Symptoms of High C-reactive Protein

High body levels of CRP mean a person has an inflammatory condition or an infection. Symptoms that may be associated with high CRP include:
What Happens If C-reactive Protein Level Is High?
Elevated CRP level can be a sign of infection, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and tuberculosis. Furthermore, it can also lead to atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, heart attack, failure or stroke.
Persistent high CRP levels may indicate ongoing inflammation or chronic disease, which could require further investigation and management. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment are crucial to address the underlying causes and prevent complications.
CausesWhat are the Causes of High C-reactive Protein?
High CRP levels can be caused by a range of conditions that trigger inflammation in the body. Common causes include:
What to Do If C-reactive Protein Is High?
Before proceeding, it is very important to know that lowering the CRP is not guaranteed to reduce the risk of autoimmune or cardiovascular disease.
Eating a nutritious and balanced diet that consists of fibre, fruits and vegetables can help lower the CRP concentration. Moreover, your doctor might suggest medications like statin or cholesterol-reducing medicines to reduce the CRP level. Vitamin C is also a way to reduce the CRP level for individuals with higher odds of cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, the preventive measures mentioned below can help you lower the C-reactive protein levels in your body –
- Increase aerobic exercises such as running, cycling or fast walking
- Quit smoking
- Lose weight
- Consume a heart-healthy diet
Therefore, individuals experiencing any changes, symptoms, or discomfort should talk to their doctor immediately. People sometimes confuse the C-reactive protein test with the high-sensitivity CRP test. Though both of these tests measure the CRP level in the body; however, the tests are done to identify different medical conditions.
What If CRP is Low?
Generally, if C-reactive protein is low, this indicates a good sign of little or no inflammation in the body. This often means you are healthy as CRP increases during inflammations, infections, and other chronic diseases.
However, CRP is mainly meant to diagnose inflammation; hence, a low level does not mean that there are no health complications but rather shows that significant inflammatory processes may be absent. Therefore, always refer to your healthcare provider for further explanation about your CRP results regarding your particular situation.
Therefore, individuals experiencing any changes, symptoms, or discomfort should talk to their doctor immediately. People sometimes confuse the C-reactive protein test with the high-sensitivity CRP test. Though both of these tests measure the CRP level in the body, the tests are done to identify different medical conditions.
Protect What Matters - Explore Other Insurance Options














