What is a Gastroscopy: Definition, Procedure, Uses and Risks
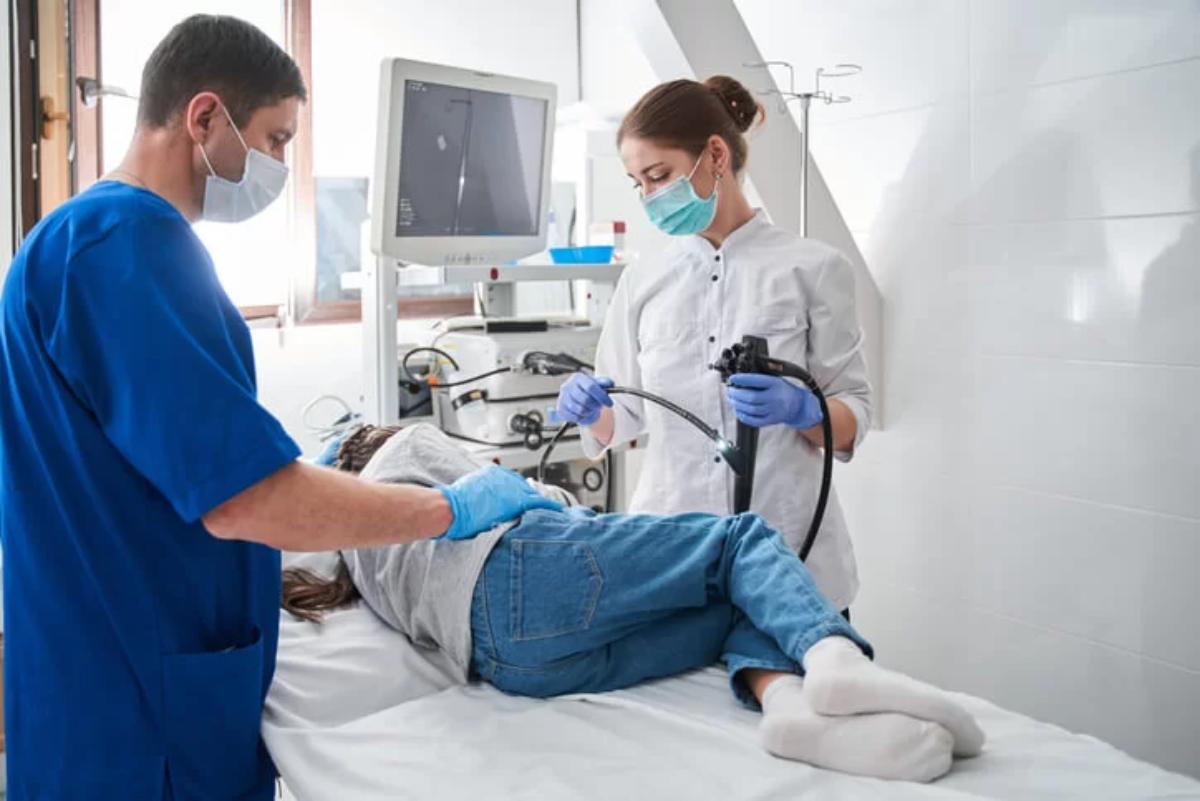
Also referred to as upper endoscopy, gastroscopy is a test to check the upper digestive tract. The procedure is performed using a thin, flexible tube, which is inserted into the patient’s mouth. This test can help diagnose your stomach problems and collect tissues for biopsy.
Read on to learn gastroscopy's meaning, its uses, the procedure for this test, risks and more.
What Is the Meaning of Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy is a medical procedure involving examining the upper digestive tract through a thin, long tube. To observe, a tube is put into the mouth and passed into the oesophagus, stomach, and first segment of the small intestine (duodenum).
A video camera and light are included in the endoscope, which sends images to the monitor for proper diagnosis.
How to Prepare for a Gastroscopy Test?
Now that you know what gastroscopy is, it is essential that you also know how to prepare for the procedure. Go through the following points to know more:
- You will need to have an empty stomach before the test. For that, your doctor would advise you to refrain from eating anything for 6 hours before the procedure.
- If you are under medication, you should consult your doctor about whether you should take it during the day of the test or skip it.
- You will have to sign a consent form before the test.
- You can also ask the doctor whether you will be put under sedation or not.
- If you wear false teeth or glasses, you will have to remove them.
How is a Gastroscopy Performed?
Generally, gastroscopy is performed on an outpatient basis. However, you may also undergo this procedure if you are admitted to a hospital. The gastroscopy procedure is mentioned in the following points:
- The technician sprays the back of your throat with local anaesthesia. This will numb the region and make swallowing the tube simpler. It might taste harsh, make you cough, and make your eyes water.
- Your throat won't start to feel numb for a few minutes. The endoscopist inserts the gastroscope into your mouth, throat, and oesophagus. The tube, which is a little larger than a pen, will feel uncomfortable but shouldn't hurt.
- They will ask you to swallow as the tube reaches down. The technician might also put a small amount of air to clearly view the inside of your oesophagus.
- After this, the endoscopists will collect tissue samples for biopsy.
The entire procedure takes about 15 minutes to finish.
What Are Some Common Uses of a Gastroscopy Test?
After knowing the procedure, you should know the uses of this test. You will be prescribed a gastroscopy test to diagnose symptoms such as:
- Chronic heartburn, vomiting or nausea.
- Stomach pain.
- Weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Suspected peptic ulcer.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Black stool or blood in your stool.
- Probable cancer of the oesophagus or stomach.
- A check-up after stomach surgery.
What are the Risks of a Gastroscopy Test?
A few possible risks may include:
- Bleeding.
- Sore throat.
- Teeth damage.
- Infection in the chest.
- Sedative reaction.
- Tear or hole.
Although these risks are very uncommon, your healthcare provider will be there to guide you if you present with any of these symptoms.
What to Do After a Gastroscopy Test?
Following the gastroscopy procedure, you could experience some bloating and pain. Typically, this lasts a few hours. If you are not under sedation, you can often go home and continue your daily activities. Before the effects of the local anaesthesia spray wear off, you won't be able to eat or drink. This process takes an hour or so.
If you underwent sedation, you should spend an hour or two in the endoscopic unit recovering. It's possible that you barely recall anything about the test. You must be driven home and spent the night by a friend or relative.
How to Prepare Yourself for Undergoing Gastroscopy?
Whether you’re about to undergo a diagnostic test like a gastroscopy test, proper preparation can help ensure accurate results and a smooth experience. Below are some essential steps you should follow to get ready for your test:
- If your doctor asks for fasting, avoid food or drinks for 8-12 hours before the test.
- Hydration is particularly important for tests; hence, consume a lot of water.
- Wear loose and comfortable clothes to make the process easier.
- Arrive early to ensure that you have enough time to complete any pre-test procedure.
- Check priorly to if gastroscopy is covered under your health insurance policy to avoid any unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
- Follow all the post-test care instructions and be sure to ask about any restrictions or aftercare required.














