9000+ Cashless Garages
1.2 Cr+ Policies Sold



Car insurance Online, Up to 90% Discount
It's a Brand New Car
What is a Camshaft in Automobiles: Types, Construction and Applications
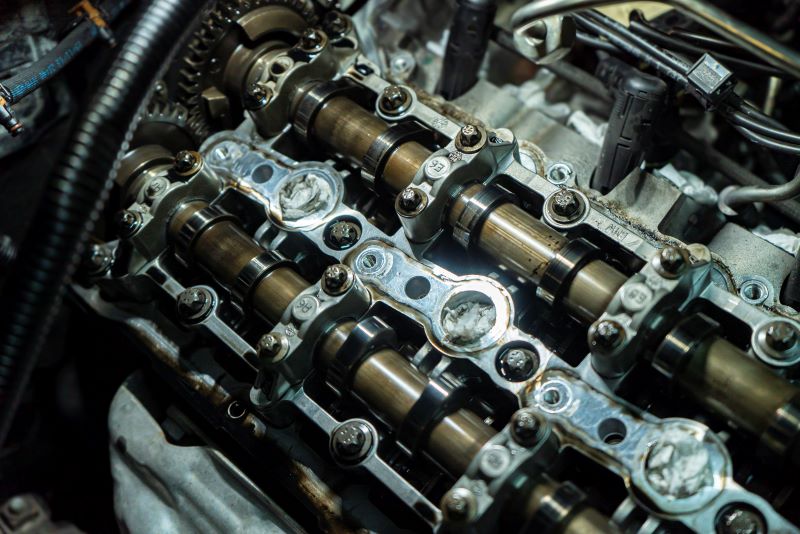
A camshaft is a mechanical component used in internal combustion engines to control the opening and closing of the engine's intake and exhaust valves. It is a cylindrical shaft with specially shaped lobes or cams along its length.
These lobes are designed to press against valve lifters, pushrods, or directly against the engine valves, causing them to open and close at precise intervals during the engine's operation.
What Is a Camshaft?
The camshaft is driven by the engine's timing mechanism, which can be a timing belt, timing chain, or gears, and it rotates at half the speed of the engine's crankshaft.
As the camshaft rotates, the lobes come into contact with the valve lifters or followers, converting the rotational motion of the camshaft into linear motion, thereby actuating the engine valves.
What Are the Functions of Camshaft?
The camshaft is a critical component of an internal combustion engine, and it serves several essential functions that play a vital role in the engine's operation.
Here are the main functions of the camshaft:
Valve Timing Control
The primary function of the camshaft is to control the opening and closing of the engine's intake and exhaust valves at specific intervals. The camshaft is designed with cam lobes or lobes that are positioned to push against the valve lifters.
As the camshaft rotates, these lobes actuate the valves, allowing air and fuel to enter the combustion chamber during the intake stroke and allowing exhaust gases to exit during the exhaust stroke.
Valve Lift Control
The shape and size of the cam lobes on the camshaft determine the amount of valve lift. A higher cam lobe profile results in greater valve lift, allowing more air and fuel to enter the engine, which can increase engine power and performance.
Valve Duration Control
The duration for which the valves stay open and closed is crucial for engine efficiency and power. The shape and arrangement of the cam lobes on the camshaft determine the valve duration. Properly timed and balanced valve duration ensures optimal engine breathing, fuel efficiency, and power output.
Valve Overlap Control
In some engine designs, the intake and exhaust valves overlap during certain points in the engine's operating cycle. This valve overlap is controlled by the camshaft and can influence engine performance characteristics, such as scavenging exhaust gases and improving low-end torque.
Camshaft Synchronisation
In engines with multiple camshafts, such as dual overhead cam (DOHC) or overhead camshaft (OHC) configurations, the camshafts must be synchronised to work in harmony. Timing belts, timing chains, or gears connect the camshafts to the crankshaft, ensuring that the valves are open and closed at the correct times concerning the engine's pistons.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Some modern engines use camshaft phasing or variable valve timing systems to adjust the camshaft's timing and control the valve events based on engine load and speed. VVT enhances engine efficiency, power, and emissions by optimising valve timing for different operating conditions.
What Is the Construction Process of a Camshaft?
The general overview of the construction process of a camshaft is mentioned below:
Material Selection
Camshafts are usually made from forged steel or cast iron. The selection of material depends on the engine's design and performance requirements.
Design and Engineering
Engineers create a design for the camshaft based on the engine's specifications, intended performance, and other factors. This design includes the shape and profile of the cam lobes, their spacing, and the overall dimensions of the camshaft.
Camshaft Blanks
The manufacturing process starts with obtaining camshaft blanks. These are typically cylindrical pieces of the chosen material that will be machined to form the final camshaft
Machining
The camshaft undergoes precision machining using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines. This involves several steps:
Turning
The camshaft blank is placed on a lathe, and excess material is removed to achieve the desired diameter and length.
Cam Profiling
The cam lobes are machined into the camshaft using specially programmed CNC machines. The profile of each lobe is based on the design specifications. This process is crucial, as the shape of the cam lobes directly affects engine performance.
Heat Treatment
After machining, the camshaft is heat-treated to improve its hardness and durability. The specific heat treatment process may vary depending on the material used.
Grinding
After heat treatment, the camshaft undergoes precision grinding to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish. This step is essential for ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear.
Finishing
The camshaft may go through additional finishing processes to ensure the highest quality. This can include polishing, shot peening and balancing to eliminate any potential imbalances that could cause vibration.
Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control checks are performed to verify that the camshaft meets the required specifications and tolerances. This is crucial to ensuring the camshaft's reliability and optimal engine performance.
Assembly
Once the camshaft is complete and has passed all quality checks, it is ready for installation in the engine. It will be positioned in the engine block and connected to the crankshaft via timing gears, belts, or chains. The camshaft's timing to the crankshaft is carefully set to achieve the desired engine performance.
How Does Camshaft Work?
Here's a step-by-step explanation of the working of the camshaft:
Step 1: Installation
The camshaft is positioned inside the engine block and is supported by bearings. It runs parallel to the crankshaft and is driven by the engine's timing mechanism, which can be a timing belt, timing chain, or gears.
Step 2: Lobes
There are several lobes, each corresponding to a specific valve in the engine. The number and shape of these lobes depend on the engine's design and the number of valves it has. In a typical four-stroke engine, you'll find one lobe for each intake valve and one lobe for each exhaust valve.
Step 3: Valve Lifters and Followers
The camshaft lobes press against valve lifters (also known as tappets) or cam followers (also called rocker arms). These components are in contact with the engine valves. The lifters or followers transfer the motion from the camshaft to the valves.
Step 4: Valve Timing - Intake Stroke
As the engine rotates and the camshaft turns, a lobe responsible for the intake valve approaches the corresponding valve lifter or follower. The lobe's shape is designed to lift the lifter or follower, causing the intake valve to open at the right moment during the engine's intake stroke.
Step 5: Valve Opening - Intake Stroke
When the intake valve opens, the engine's piston moves down, creating a low-pressure area inside the cylinder. This allows the air-fuel mixture to be drawn into the cylinder from the intake manifold.
Step 6: Valve Timing - Compression Stroke
After the intake stroke, the camshaft continues to rotate. The intake valve closes due to the shape of the cam lobe, sealing the combustion chamber.
Step 7: Valve Timing - Power Stroke
As the engine piston moves up during the compression stroke, another cam lobe corresponding to the exhaust valve approaches its lifter or follower. This lobe lifts the lifter, opening the exhaust valve at the right time.
Step 8:Valve Opening - Exhaust Stroke
With the exhaust valve open, the burnt fuel-air mixture is expelled from the cylinder and pushed into the exhaust manifold as the piston moves down during the power stroke.
Step 9: Valve Timing - Exhaust Stroke
After the power stroke, the exhaust valve closes due to the camshaft's rotation, sealing the exhaust port.
Step 10: Repeating the Cycle
The camshaft continues to rotate, repeating this process for each cylinder in the engine. This series of events happens rapidly, coordinating the intake and exhaust valve timings for optimal engine performance.
What Are the Types of Camshafts?
There are several types of camshafts used in internal combustion engines, each designed to suit specific engine configurations and performance requirements.
1. Flat-Tappet Camshaft
The flat-tappet camshaft is a traditional design with flat lobes that make direct contact with the lifters (tappets) in the engine's valve train. It is commonly used in older pushrod engines and some modern engines with less aggressive valve lift profiles.
2. Roller Camshaft
Roller camshafts have cylindrical lobes with small rollers at the base of each lobe. These rollers reduce friction between the cam lobe and the lifters, allowing for smoother operation and less wear. Roller camshafts are often found in high-performance engines and modern overhead valve engines.
3. OHC (Overhead Camshaft)
In OHC engines, the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the cylinders. It directly actuates the valves through cam followers (lifters), pushrods, or rocker arms. OHC camshafts are known for their ability to provide precise valve control and high RPM capabilities.
4. DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft)
DOHC engines have two camshafts per cylinder bank—one for the intake valves and one for the exhaust valves. This configuration allows for more precise valve timing and greater valve lift control, making DOHC engines common in high-performance and high-revving applications.
5. SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft)
SOHC engines have one camshaft per cylinder bank, actuating both the intake and exhaust valves through a combination of cam lobes and rocker arms. While simpler and less expensive than DOHC engines, SOHC engines may have some limitations in valve control and RPM potential.
6. VVT (Variable Valve Timing) Camshaft
Some modern engines are equipped with variable valve timing systems that can adjust the camshaft's timing to optimise valve events based on engine load and speed. This technology allows for improved engine efficiency, power, and emissions.
7. Camshaft Phasers
Camshaft phasers are components used in engines with variable valve timing systems. These phasers can adjust the position of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft, altering valve timing and lift for different engine operating conditions.
8. Hydraulic Lifter Camshafts
Hydraulic lifters are components that maintain zero valve lash automatically, ensuring proper valve clearance. Camshafts designed for hydraulic lifters have specific cam profiles to accommodate this characteristic.
What Are the Differences Between Single and Double Overhead Camshafts?
The table below provides more insight on the differences between single and double overhead camshafts.
| Basis of Difference | Single Overhead Camshaft | Double Overhead Camshaft |
| Definition | In a SOHC engine, there is a single camshaft located in the cylinder head, which actuates both the intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder through a combination of cam lobes, rocker arms, and sometimes, pushrods. | In a DOHC engine, there are two camshafts per cylinder head—one for the intake valves and another for the exhaust valves. Each camshaft directly actuates the valves of its respective type without the use of pushrods or rocker arms. |
| Valve Control | With a single camshaft, the timing and lift of both the intake and exhaust valves are controlled by the same camshaft. This can limit the degree of valve timing control and potential engine performance compared to DOHC configurations. | In DOHC engines, having separate camshafts for intake and exhaust valves allows for precise and independent control of valve timing and lift. This provides greater flexibility in tuning the engine for improved performance and efficiency. |
| Valve Actuation Complexity | The valve train in SOHC engines may involve rocker arms or pushrods, which can introduce additional components and complexity compared to DOHC setups. | DOHC engines generally have a more straightforward valve actuation mechanism since each camshaft directly actuates the valves without intermediary components. |
| Engine Size & Layout | SOHC engines tend to be more compact and lighter due to the single camshaft design. They are often used in smaller, less performance-oriented vehicles. | DOHC engines are commonly found in performance-oriented vehicles and larger engines where precise valve control is crucial for optimal performance. |
| Cost of Manufacturing | Generally, SOHC engines are less expensive to manufacture and maintain due to their simpler design and fewer components. | DOHC engines typically involve more components and are more complex to manufacture, making them costlier than SOHC engines. |
What Are the Reasons for Failure of Camshaft?
Several factors can contribute to the failure of a camshaft, as mentioned below:
Lack of Lubrication
Adequate lubrication is crucial for the camshaft's proper operation. If the engine's oil supply is compromised due to low oil levels, oil pump failure, oil starvation during aggressive driving or extreme angles, or clogged oil passages, the camshaft can experience excessive friction and wear. Moreover, insufficient lubrication can lead to cam lobe and lifter wear and, in severe cases, camshaft seizure.
Poor Maintenance
Neglecting regular engine maintenance, such as infrequent oil changes or using low-quality oil, can accelerate wear and lead to premature failure of the camshaft.
Contaminated Oil
Contaminated oil containing particles, debris, or sludge can damage the camshaft surfaces and cause excessive wear over time.
Camshaft Material Defects
In rare cases, manufacturing defects or material quality issues can lead to weakened or brittle camshaft surfaces, making them more prone to failure.
Overheating
Engine overheating due to cooling system failures or other issues can cause thermal stress and warping of the camshaft, leading to premature failure.
Improper Installation
Incorrect installation of the camshaft, such as improper alignment or incorrect torque settings, can put excessive stress on the camshaft and lead to failure.
What Are the Differences Between Camshaft and Crankshaft
Follow the table to understand the basic difference between a camshaft and a crankshaft:
|
Basis of Difference |
Camshaft |
Crankshaft |
|
Functionalities |
The camshaft is responsible for controlling the opening and closing of the engine's intake and exhaust valves. It determines the valve timing and lift, which regulates the air-fuel mixture intake and the expulsion of exhaust gases during the engine's four-stroke cycle. |
The crankshaft's primary function is to convert the reciprocating motion of the engine's pistons into rotational motion. It converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into a rotary motion, which drives the vehicle's wheels or powers other mechanical devices. |
|
Location |
This is typically located within the cylinder head of the engine. |
This is located in the engine block and extends through the engine's crankcase. |
|
Design and Construction |
Camshafts have cam lobes or lobes that are specifically shaped to actuate the valves. The cam profile determines the valve lift and duration, which affects engine performance. |
Crankshafts have crankpins and throws that are designed to convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion. |
|
Rotational Speed |
This typically rotates at half the speed of the crankshaft in a four-stroke engine (i.e., one camshaft revolution for every two crankshaft revolutions). |
The crankshaft rotates at a speed directly proportional to the engine's RPM (revolutions per minute). |
What Are the Advantages of Camshaft?
The camshaft offers several advantages in the operation of an internal combustion engine. Here are the main advantages of using a camshaft in an engine:
Precise Valve Timing
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine's intake and exhaust valves at specific intervals, known as valve timing. Precise valve timing ensures that the valves open and close at the right moments during the engine's four-stroke cycle, optimising combustion efficiency and power output.
Valve Lift Control
The shape and size of the cam lobes on the camshaft determine the valve lift. Higher cam lobe profiles result in greater valve lift, allowing more air and fuel to enter the engine, which can lead to increased engine power and performance.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Some modern engines use camshaft phasing or variable valve timing systems to adjust the camshaft's timing and control the valve events based on engine load and speed. VVT enhances engine efficiency, power, and emissions by optimising valve timing for different operating conditions.
Improved Exhaust Gas Flow
The camshaft also controls the timing of the exhaust valve, allowing for the timely expulsion of exhaust gases during the exhaust stroke. This efficient exhaust gas flow helps reduce back pressure and enhances engine performance.
Adaptability for Different Engine Designs
Camshafts can be designed to suit various engine configurations, such as overhead cam (OHC), dual overhead cam (DOHC), or single overhead cam (SOHC) layouts, making them adaptable to different engine types.
What Are the Disadvantages of Camshaft?
While the camshaft provides numerous advantages in the operation of an internal combustion engine, it also has some disadvantages and limitations. Here are some of the main disadvantages of using a camshaft:
Fixed Valve Timing
Traditional camshafts have fixed profiles, meaning their valve timing and lift characteristics are constant. This fixed design may not be optimal for all engine operating conditions, limiting the engine's efficiency and performance potential.
Limited Adjustability
Conventional camshafts cannot dynamically adjust valve timing and lift on the fly. As a result, they may not fully exploit the engine's potential across a wide range of operating conditions.
Variable Load Performance
Camshafts are designed with specific valve profiles for optimal performance at certain engine loads and speed ranges. They may not perform optimally under light or heavy load conditions, potentially affecting engine efficiency.
Mechanical Friction
The interaction between the camshaft lobes and valve lifters introduces mechanical friction, which can lead to wear over time and necessitate periodic maintenance and replacement.
What Are the Different Applications of Camshaft?
To answer “What is the use of camshafts”, know that these have numerous applications in various internal combustion engines, providing precise valve control and facilitating the engine's proper functioning. Here are some of the primary applications of camshafts:
Automobile Engines
Camshafts are extensively used in automobile engines to control the timing and lift of the intake and exhaust valves. They play a crucial role in regulating the air-fuel mixture intake and the expulsion of exhaust gases, optimising engine performance, power, and fuel efficiency.
Motorcycle Engines
These are fundamental components in motorcycle engines, serving the same purpose as in automobile engines. They control the timing and lift of the intake and exhaust valves to improve engine efficiency and performance.
Heavy-Duty Engines
Camshafts are also employed in heavy-duty engines used in trucks, buses, construction equipment, and other industrial applications. These engines rely on precise valve timing and lift to handle high loads and deliver optimal power output.
Marine Engines
Camshafts are used in marine engines to regulate valve timing and lift, ensuring efficient fuel combustion and power delivery in boats and other watercraft.
Aircraft Engines
Camshafts are found in certain aircraft engines to control valve actuation and optimise engine performance during flight.
Diesel Engines
Camshafts are crucial components in diesel engines, controlling the timing and lift of the intake and exhaust valves. They help regulate fuel injection and exhaust gas recirculation, optimising fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Overall, camshafts are critical components in various types of internal combustion engines, ensuring precise valve control, efficient fuel combustion, and optimal engine performance. Their applications span a wide range of industries, including automotive, transportation, industrial machinery, and power generation.
Explore Insurance Coverage for Your Vehicle













