List of 26 Diseases Caused by Fungi

Diseases caused by fungi are responsible for the death of more than 1.5 million people, even when these diseases are easily avoidable. These diseases can affect everyone; hence, individuals must have a thorough knowledge of them to prevent serious complications.
These diseases often go undiagnosed despite how common they are, which delays treatment. Read on to know about diseases caused by fungi, symptoms, effects, treatment and many more!

Table of Contents

What are Fungal Diseases?

Mycoses is a term used to refer to fungal diseases and infections caused by fungi, which exist in yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. The infections can affect many body parts, including internal organs like the lungs, skin, and nails. From mild conditions to life-threatening disorders, mycoses can be presented differently.
Some areas of the body are more prone to infection because of a warm and moist environment that provides favourable conditions for fungus growth. Antifungal medicines usually cure these diseases but must be diagnosed before complications. Because of their atypical symptoms, most people do not identify fungal infections early, leading to severe health problems.
What are the Causes of Diseases Caused by Fungi?
Several diseases caused by fungi also result from the entrance of fungal pathogens into the body, which can be achieved via inhalation, skin contact or food. This infection usually occurs when a person's immune system does not function well; hence, people become vulnerable to such fungi.
The growth of mould and dampness exposure are major factors contributing to the development of fungal diseases. Besides, some medical treatments like immunosuppressive drugs or antibiotics kill our bodies' defence mechanisms that are supposed to keep us safe against fungi.
Moreover, a few fungi reside on the skin and mucosal surfaces naturally, but an imbalance in this system leads to overgrowth and subsequent infection. Likewise, poor hygiene practices, close association with sick people and underlying conditions such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS increase the risk of further attacks from fungi.
26 Diseases Caused by Fungi
Fungi are single-celled or multi-celled eukaryotic organisms that are present in the environment. Some fungi (mushroom) are visible to the naked eye, and others are tiny, microscopic (yeast) thus can be found in a multitude of forms.
Following are some of the diseases caused by fungi,
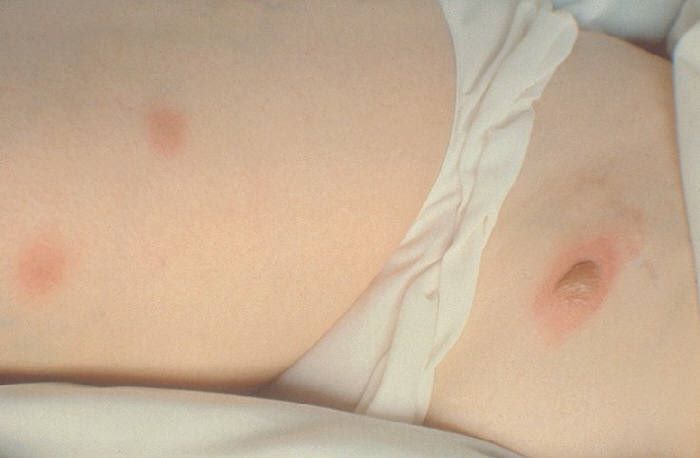
- Candidiasis: Candida species cause this infection that can attack the mouth, throat and genital areas, resulting in symptoms like white patches, itching and discomfort. In extreme cases, it may go to blood flow, leading to death.
- Blastomycosis: This fungal disease is caused by Blastomyces species, mainly affecting the lungs and causing flu-like symptoms such as fever, cough, and chest pain. It can spread to other body sites, including the skin and bones.
- Histoplasmosis: This infection is mainly found in the lungs resulting from inhaling spores of a fungus called Histoplasma; its most common respiratory symptoms are coughing and shortness of breath.
- Aspergillosis: This infection, which is caused by the fungus Aspergillus, may result in certain diseases, starting from simple allergic reactions to serious lung infections. It is common in people with weak immune systems and pre-existing lung problems.
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever): Inhalation of soil spores with Coccidioides fungus leads to this illness, presenting symptoms such as fever, a cough or even fatigue. Arid regions are its common occurrence places.
Depending on the fungi and other factors, diseases can be of different types. These are as follows:
Fungal Diseases that Are Most Common
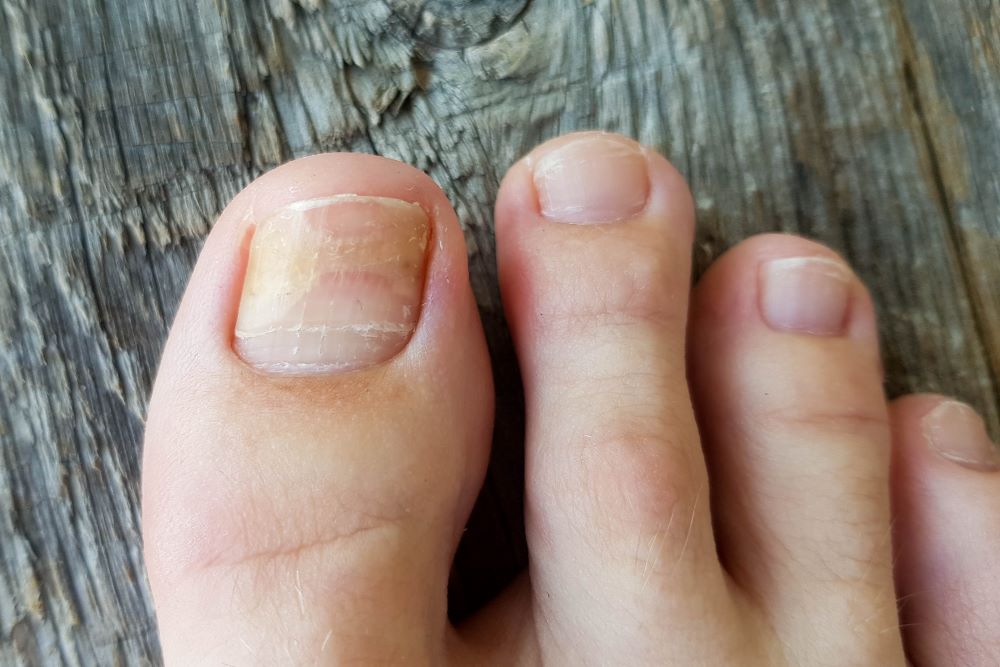
- Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): This fungus causes this critical lung infection that mainly affects individuals with weak immune systems, like those who have HIV/AIDS, leading to severe respiratory distress and possible death if untreated.
- Fungal Nail Infections: These infections make nails discoloured, thickened, and brittle, often resulting in pain and discomfort. They usually affect toenails and are difficult to treat. In some cases, it may take longer periods of antifungal therapy.
- Vaginal Candidiasis: It is a common yeast infection caused by an overgrowth of fungi in the vagina. This results in itching, burning, and a white discharge. Factors like antibiotics and weakened immunity can initiate the infection.
- Candida Infections of the Mouth, Throat, and Oesophagus: They are responsible for white or creamy patches on the tongue, inner cheeks and throat, causing soreness and difficulty swallowing.
Ringworm (a Communicable Disease Caused by Fungi): A contagious fungal infection of the skin, scalp, or nails characterised by red, scaly, itchy patches which are often circular. It can also be transmitted through direct contact.
Fungal Diseases that Affect People with Poor Immunity System
- Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): One serious lung disease is PCP, which is caused by a fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii in people with weakened immune systems, especially those living with HIV/AIDS.
- Candidiasis: Candidiasis is an infection which is caused by Candida species, often leading to oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, or systemic infections in individuals who are immunocompromised.
- Aspergillosis: Aspergillus fungi infection leads to severe respiratory symptoms, particularly among people suffering from lung diseases or having low or weak immunity.
- Talaromycosis: HIV/AIDS patients in Southeast Asia are usually affected by Talaromycosis, an infection caused by Talaromyces marneffei, and it can lead to life-threatening systemic illness.
- Candida Auris Infection: Candida auris is a fungus that is multidrug-resistant and renowned for its ability to spread in healthcare facilities, presenting a significant threat to persons with weakened immune systems.
- Invasive Candidiasis: When yeast enters the bloodstream, it results in invasive candidiasis, which can cause serious infections in organs like the brain, heart, eyes and bones, especially among people whose immunity has been compromised.
- Cryptococcus Neoformans Infection: Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungus that causes severe brain infection (cryptococcal meningitis) that mainly affects individuals who have weak immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
Mucormycosis: Mucormycosis is an aggressive but rare fungal infection caused by Mucorales fungi affecting sinuses, lungs or brain, predominantly in patients with diabetes under poor control or immunosuppression.
Fungal Disease Caused Due to Living in Specific Area or While Travelling
- Blastomycosis: This infection is prompted by Blastomyces species, which are found in damp earth and decaying wood in areas of the North American continent. It majorly affects the lungs but can spread to other organs.
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever): Caused by Coccidioides fungi, this condition is endemic to dry areas such as southwestern parts of the United States. Its primary organ affected is the lung, causing flu-like symptoms and can eventually become chronic.
- Histoplasmosis: This disease results from inhaling spores of Histoplasma fungi that often occur in bird and bat droppings within regions like the Ohio-Mississippi River valleys. It may cause mild to severe respiratory problems.
- Cryptococcus Gattii Infection: Found in tropical and subtropical regions and the Pacific Northwest, Cryptococcus Gattii results in lung and brain infections. It can result in severe respiratory symptoms and fatal meningitis.
- Paracoccidioidomycosis: This disease is endemic to Latin America and is caused by Paracoccidioides fungi that mainly affect the lungs. It may disseminate into other organs, leading to chronicity, especially among agricultural workers.
Other Fungal Diseases
- Fungal Eye Infections: The eyes are sometimes attacked by fungi that cause keratitis or fungal eye infections. This occurs when they invade the cornea as a result of an injury to the organ or improper handling of contact lenses.
- Mycetoma: Mycetoma is a slowly progressive chronic infection which mainly affects the skin, subcutaneous tissues and bones, especially on the feet. It will be shown to have no pain but very large swellings with discharge from which grains emerge.
- Sporotrichosis: Sporotrichosis, also known as rose gardener's disease, is caused by a fungus known as Sporothrix schenckii. It commonly affects the skin after minor cuts made by thorns. Usually, it appears as nodules or ulcers on the lymphatic vessels.
The above section provides the list of diseases caused by fungi. Now, let's learn about the symptoms of these diseases.
The diseases caused by fungi have their individual signs and symptoms. The symptoms of different fungal diseases are given in the table below:
Damages Caused by Fungi in Humans

The effects of fungal diseases can prove to be severe for people with poor immunity systems. It means those who are suffering from HIV/AIDS or who are undergoing chemotherapy and taking steroid medication have a higher chance of getting affected by fungal disease.
These diseases can spread to vital organs such as the brain and heart and can result in serious complications. These are as follows:
- Endocarditis: This is an infection of the heart valves by fungi that leads to vegetation formation and damage to heart tissue. It can lead to heart failure and embolism and can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
- Meningitis: It arises when fungi cause infection in the meninges, the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This can lead to symptoms such as headaches, neck stiffness, fever and neurological harm or death.
- Nephritis: This is a kidney infection caused by fungi, which inflames and damages kidney tissues. The symptoms include back pain, blood in urine, and fever. It may eventually progress into renal failure if not appropriately managed.
- Abscess Formation: These infections can cause the formation of abscesses, when a pus pocket forms in tissues or organs, leading to localised discomfort, swelling and fever. These abscesses may happen in different body parts, including the brain and the lungs.
- Organ Failure: Fungal infections spreading into important body organs cause significant inflammation and tissue destruction, culminating in organ failure. Lungs, liver or kidneys are some of the organs affected by this, which could be fatal.
Risk Factors Associated With Diseases Caused by Fungi
Certain environmental or health conditions trigger fungal diseases. These are as follows,
- Humidity and dampness
- Inadequate blood flow
- Poor immunity system
- Effects of certain medication such as antibiotics, long-term usage of corticosteroids
- Chemotherapy/radiation
- Individuals who have undergone organ transplantation
- Infancy/aging
There are various methods to diagnose and identify the diseases that are caused by fungi. Below is a table which shows how these infections are diagnosed:
When diagnosed with fungal disease, doctors might prescribe some topical antifungal ointments, antiseptic mouthwash and medication depending on the type of fungal disease.
What Are the Preventive Measures to Control Fungal Diseases?
Individuals can prevent fungal infection by following the tips mentioned below,
- Wash hands regularly, especially after touching animals or people suffering from some diseases.
- Do not use other people's clothes, towels, comb or other skincare products.
- Keep skin clean especially fold areas of your body.
- Do not walk barefoot in locker rooms, community shower rooms.
- When touching plants and dirt, put on protective clothing.
- Antifungal disinfectants can be used to reduce fungal contamination on surfaces.
- Athlete's feet can be avoided by wearing breathable shoes and keeping feet dry.
- Regular medical check-ups and screenings for infection should be conducted.
Does Health Insurance Cover Fungal Diseases?
There is no insurance standard for treating fungal infections, but most health insurance policies cover diagnosing and treating such diseases. They include:
Medical Need: Almost all medical plans have provisions for the diagnosis, treatment, and tests of fungi only when found to be medically necessary, including visits to see doctors, outpatient services, prescribed antifungal drugs and radiological examinations.
Types Of Coverage For Fungus Diseases
- Diagnostic Tests: These will comprise the cost of mycology cultures, biopsies, and serology blood tests.
- Medications: Insurance companies cover both oral and topical prescription antifungal medications.
- Hospitalisation: When hospitalisation or surgical procedures are necessary because of a fungal infection.
Prophylactics: Insurance may not cover some preventive measures like antifungal prophylaxis in high-risk situations unless advised by a physician.
To determine the exact coverage, it’s best to review the health insurance policy details and contact your insurance provider for specific information related to fungal disease treatment and coverage.














