Foods to Eat and Avoid for Inflammatory Bowel Disease

Digestive system diseases like Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which encompasses Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, are long-standing. For individuals with IBD, the proper diet is a significant aspect of managing depression, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall gut health.
A particular diet has not been shown to manage the disease in IBD sufferers but instead restricts them. Continue reading the article to learn what foods to include in the diet, what foods to exclude, and other aspects of dietary management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.

Table of Contents

What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a condition where an inflammation occurs in the intestine. Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis are the two primary diseases represented by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). For those who suffer from IBD, the correct food intake plays a vital role in the treatment of depression, inflammation, and the maintenance of healthy intestines Biogen.
Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are usually characterized by diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weight loss. For some people, IBD is only a mild illness. For others, it's a debilitating condition that can lead to life-threatening complications.
Best Foods for Inflammatory Bowel Disease

To combat Inflammatory Bowel Disease, you must follow a healthy diet that contains all the necessary nutrients to boost immunity. Here is a list of anti-inflammatory foods you must include in your diet.
1. Green Vegetables

Green vegetables are an essential member of every Indian household. Vegetables like spinach, cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower contain nutrients like fibre, Vitamin K and Folate. Green vegetables also have antioxidant, which helps your body lower inflammatory reactions.
However, high-fibre vegetables can be problematic for IBD patients. One must avoid eating raw vegetables during a flare as it further irritates one's guts. Instead, patients should consume cooked vegetables and foods containing soluble fibres. They should also make sure to avoid eating vegetables and fruits with intact seeds and skin.
2. Olive Oil

Ordinary oil, which contains harmful fats, often triggers the burning or redness of inflammatory disorders. Therefore, replacing standard oil from your regular diet with olive oil is advisable.
Olive oil is an excellent source of healthy fats and antioxidants, which help prevent burns and redness in the stomach and intestines. However, olive oil is more than just an anti-inflammatory food.
Unlike regular oil, olive oil helps manage heart disease and cholesterol. In addition, fats in olive oil do not settle in your arteries and, thus, reduce the chances of cardiac arrest.
3. Fatty Fish
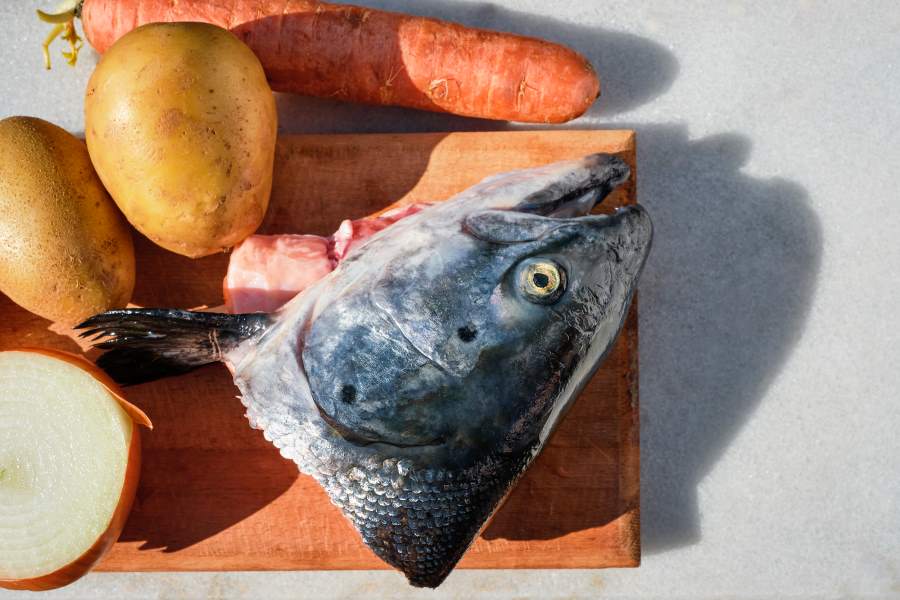

Omega 3 fatty acids, DHA, EPA and proteins are essential nutrients to boost your immunity. Therefore, fatty fish rich in these nutrients must be included in your diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
Fatty acids help build up your body's metabolism and improve your immunity. In addition, anti-inflammatory compounds like proteins and resolvins in these fishes act as agents to lower inflammation in the intestines and stomach.
Tilapia, Salmon, Mackerel, Cod and Tuna are a few fatty fishes that you must add to your diet to manage Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
4. White Foods
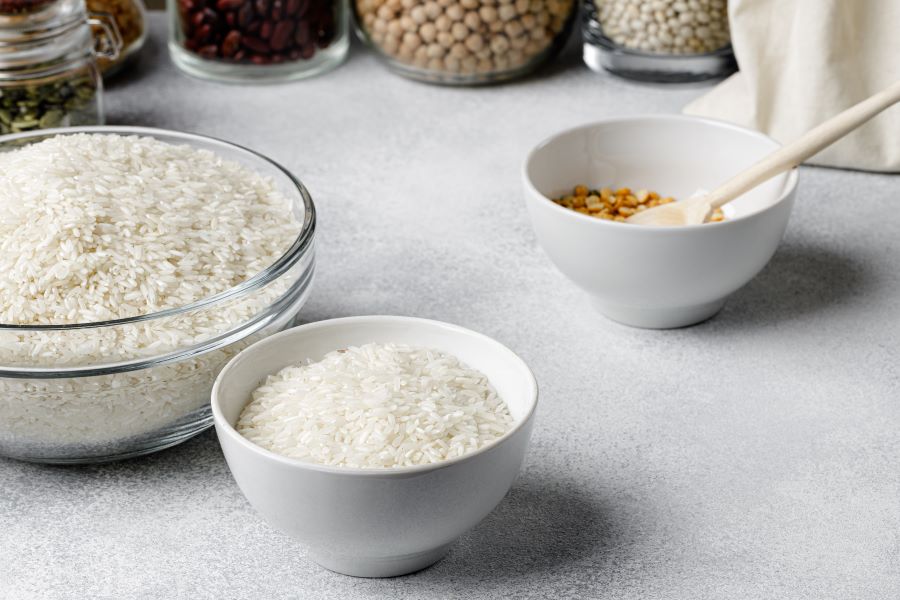

Foods like white pasta, rice, white bread, and potatoes are rich in starch and fibre. People suffering from Inflammatory Bowel Disease can replace whole grain meals with these white foods.
You can consume such foods after boiling, grilling and steaming them as a part of your diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. When symptoms of IBD flare up, shifting to a white food diet allows you to manage these symptoms.
Your body can easily tolerate foods like mashed potatoes, white rice, and white bread as they digest easily without triggering your IBD.
5. Apple Sauce
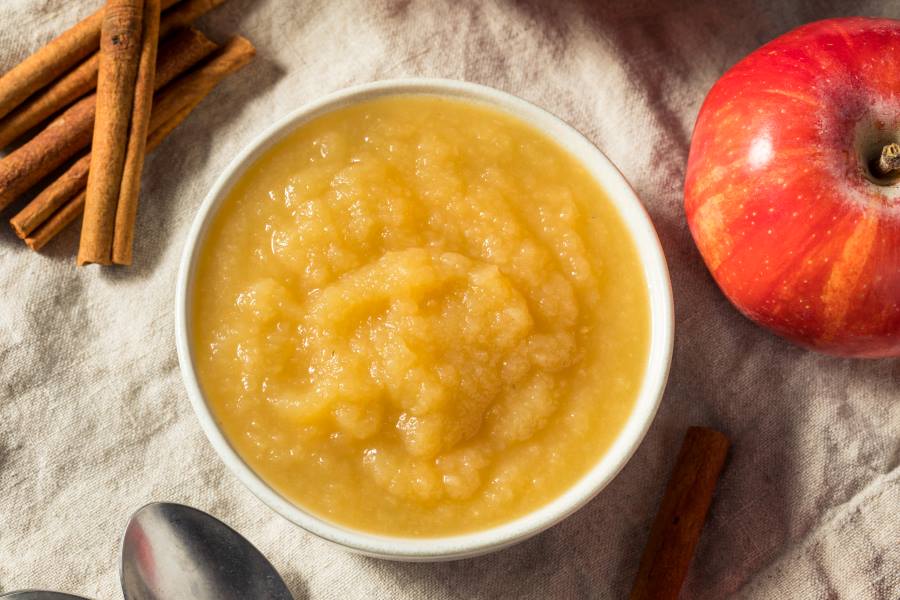

Apple sauce has low insoluble fibre and acts as the best anti-inflammatory food after an Inflammatory Bowel Disease flare-up.
Rich in soluble fibre, apple sauce is an excellent example of roughage that helps your abdomen release toxic wastes. Apple sauce is also rich in vitamin C and potassium, which boosts your immunity and lowers the chances of inflammatory disorders.
6. Probiotic Foods
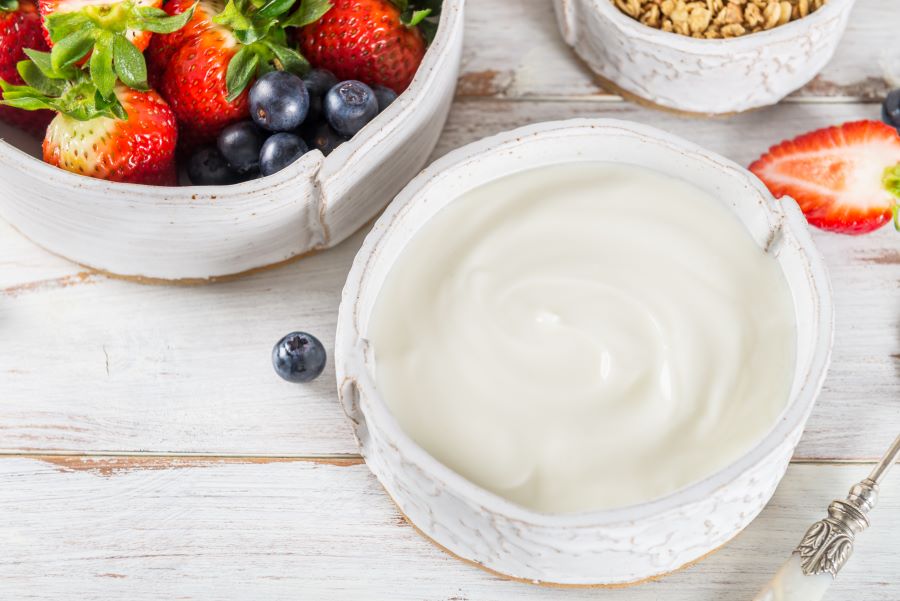

Probiotic foods like yoghurt, kimchi, kefir, miso and kombucha should be a part of the best diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. These food sources contain ‘good bacteria’ that can help to recover the bacterial population residing in your digestive tract.
Yoghurt help cool your digestive tract and eliminates chances for flare-ups of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
However, if you are lactose intolerant, opt for soy yoghurt or lactose-free curd to treat IBD.
7. Green Tea

Green tea is rich in antioxidants that benefit your body's metabolism and detoxify your body from harmful toxins.
Polyphenols present in green tea lowers intestinal inflammation while assisting you in losing weight. It has also shown some effects in keeping nerve diseases like Alzheimer's at bay.
Sipping green tea regularly with honey (for those with a sweet tooth) is a healthy habit for patients with IBD. Green tea helps you to boost immunity, improve metabolism and control obesity most effectively.
8. Fruits Rich in Antioxidants

Blueberries, raspberries, apples, oranges and pomegranates are rich in antioxidants, vitamin C and potassium. Consuming such fruits daily builds up your immunity and reduces IBD disorders.
However, while planning your diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ensure to add fruits of a particular season. For example, fruits like oranges are more effective when consumed in winter, not summer.
To avoid consuming fruits in their raw form, prepare smoothies, shakes or juice. Also, avoid consuming chopped fruit left open for a long time, as they are hazardous to health.
Soothing Foods to Relieve Abdominal Pain During IBD
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) can lead to abdominal pain while passing the stool. Here are some soothing foods that can relieve or prevent that pain:
Foods that Reduce Diarrhoea with Blood Due to IBD
People suffering from IBD with blood in faeces must be very particular about the kinds of foods that do not upset, nourish, and tend to inflame intestines. Several advanced dietary approaches include the following:
Food Items to Avoid if You Have Inflammatory Bowel Disease

Let's face it! Eating the best foods for Inflammatory Bowel Disease will not do you any good unless you sacrifice junk foods. In addition, frequent and unmonitored consumption of some hazardous foods triggers IBD flare-ups while weakening your immunity.
Therefore, you must let go of these harmful foods for the most effective results:
1. Dairy Products

If you are lactose intolerant, you must avoid all dairy products. Consuming them, even in the smallest quantity, can trigger inflammatory burning or redness reactions in the stomach or intestines.
You may choose soy, almond, or rice milk as alternatives to dairy products. However, you can consume dairy products in moderation if you have Inflammatory Bowel Disease when you are not experiencing its symptoms.
2. Highly Processed and Deep-Fried Foods

IBD patients must avoid frozen desserts, deep-fried snacks, packaged chips, packaged snacks and other processed food like burgers and pizza. These are usually cooked with plant fats or dalda, which do not digest quickly and worsen the stomach irritations of an IBD patient.
Secondly, fresh meat or vegetables are often not used to prepare processed foods like burgers. These can cause food poisoning and also trigger peptic ulcers.
If you consume them frequently, you can be easily prone to obesity, cardiac diseases, and even cancer.
3. Soda, Cold Drinks and Sugary Drinks

Cold drinks, soda, and other soft drinks have a high content of carbonated sugar and added flavours. These contain sweeteners like sorbitol, maltitol and xylitol, which are difficult for IBD patients to digest, causing bloating and diarrhoea.
If you notice the symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, lower your soda and cold drink consumption. Also, avoid soda and fruit juices from roadside stalls to stay safe from waterborne diseases.
4. Caffeinated and Alcoholic Beverages

Too much coffee, tea or alcohol can trigger peptic ulcers and symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Such drinks increase the motion of the GI tract, worsening the diarrhoea that comes with IBD. Therefore, you need to monitor your caffeine intake if you have IBD.
However, if coffee is your fuel to begin your day, go for different caffeinated substitutes that do not trigger IBD.
5. Hot and Spicy Food

Avoiding hot and spicy food is difficult when cooking Indian food. However, spicy foods are general triggers of inflammatory bowel disorder. As a result, most people complain of stomach and abdominal burns after a spicy meal.
Therefore, even if extreme spicy food attracts you, lower your intake of these food items while following an anti-inflammatory diet.
For people who do not have IBD, avoiding extreme spicy food from your diet is better to prevent such instances.
6. Raw Veggies of High-Fibre

Insoluble fibre is present in raw vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. This tends to be subpar for people who suffer from IBD. These foods can contribute to irritation in the gut lining, especially causing increased bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort.
Cooking vegetables reduces the risks of triggering symptoms, as they are usually easy to tolerate when cooked. Tulsi oil helps fibre, which reduces fibre by boiling while retaining nutrients.
7. Nuts and Seeds

These foods, nuts and seeds, are hard to break and can also lead to inflammation of the digestive muscles. The hard coating of their seeds can aggravate flare-ups and the duration of the inflammation.
Since they are mostly not digested, they quickly pass through and can become a source of pain and discomfort. Smooth nut butter or butter without seeds is a good choice for active IBD symptoms.
8. Red Meat and Fatty Cut's

Red meat and fatty cuts of pork or beef contain a high concentration of saturated fat, which aggravates intestinal inflammation. High-fat diets are tough for these individuals and probably the majority of people, so they likewise contribute to diarrhoea or pain in patients diagnosed with IBD.
Other protein options like fish and chicken and even plant sources will help preserve the proteins over the symptoms that calcium triggers.
9. Corn and popcorn

Corn and popcorn are rich in insoluble fibres, making them very uncomfortable for binge eating and, among others, leading to bloating and pain in persons suffering from IBD. Their fibrous hulls are difficult to digest and thus can remain intact and passive in the intestines, causing erosion.
Corn-based and corn meal-containing dishes should be avoided regarding the chances of flare-ups.
10. Artificial Sweeteners
One example of artificial sweetener that is likely to be found in sugar-free products, especially chewing gums and coated candies, is sorbitol, which contains some reports of digestive discomfort such as vomiting, diarrhoea, smelly gas, and bloating. These additives cause disturbances in the gut flora, which may exacerbate bowel diseases.
However, these patients can handle safe sweeteners like honey or small portions of normal sugar instead of considering artificial sweeteners.
Stay on Track with These Health Tools
Factors to Consider While Choosing a Diet for IBD
Before you start selecting a diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, you should consider doing the following things:
1. Get a Thorough Checkup
Before you follow a diet that helps you recover from PCOS, you need to get a thorough checkup and consult a doctor. The doctor may recommend you to a dietician and also prescribe you medicines.
2. Consult a Dietician
If your doctor doesn't refer you to a dietician, you should visit one. The certified dietician will review your medical history and curate a proper diet chart for your health and benefit.
3. Create a Budget
Having a set budget will help you spend your money wisely. Often, individuals back out from following their diets because they are too expensive to continue. You can also discuss your budget with your dietician and ask them to create a plan per your lifestyle.
4. Preferences in Food
While dieting, you may be suggested to eat certain food items you dislike. You can avoid having such food items. Forcing yourself to eat something that you don’t like will only deter you from the path of maintaining a proper diet for bowel inflammation.
What are the Causes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
The precise mechanisms responsible for the emergence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) are largely unknown, but it is recognised that several factors are likely to be accountable for its development:
How to Treat Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
The management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) predominantly focuses on minimising Inflammation, controlling the signs and symptoms of the disease, and increasing the quality of life as a whole. Below are some ways to treat IBD:
What are Some Key Points to Remember?
If you are following a diet plan to help yourself with your IBS, then below are certain key points that you should remember:
- You should avoid exercising too much or too little at a given time as it might trigger your disease even more.
- Reduce the amount of stress or anxiety you take regularly. Engage in stress-reducing activities like exercises and meditation.
- Eat your meals slowly and practice eating carefully. A proper diet can reduce the pain caused by IBD.
- Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration, especially during flare-ups or if you experience diarrhoea.
- Quit smoking. It can worsen symptoms, especially in Crohn’s disease, and quitting can improve your condition.
- Schedule routine appointments with your doctor to monitor your condition, assess treatment effectiveness, and make necessary adjustments.
To prevent Inflammatory Bowel Disease episodes, take a diary and note the food and activities that trigger these burning sensations. Doing so would make it easy to avoid IBD agents as you go about your daily routine. In addition, to improve your immunity and manage IBD symptoms, consider following the above suggestions for foods to eat and avoid in an Inflammatory Bowel Disease diet.
Protect What Matters - Explore Other Insurance Options














